Marbles In Cylinder Lab Answers

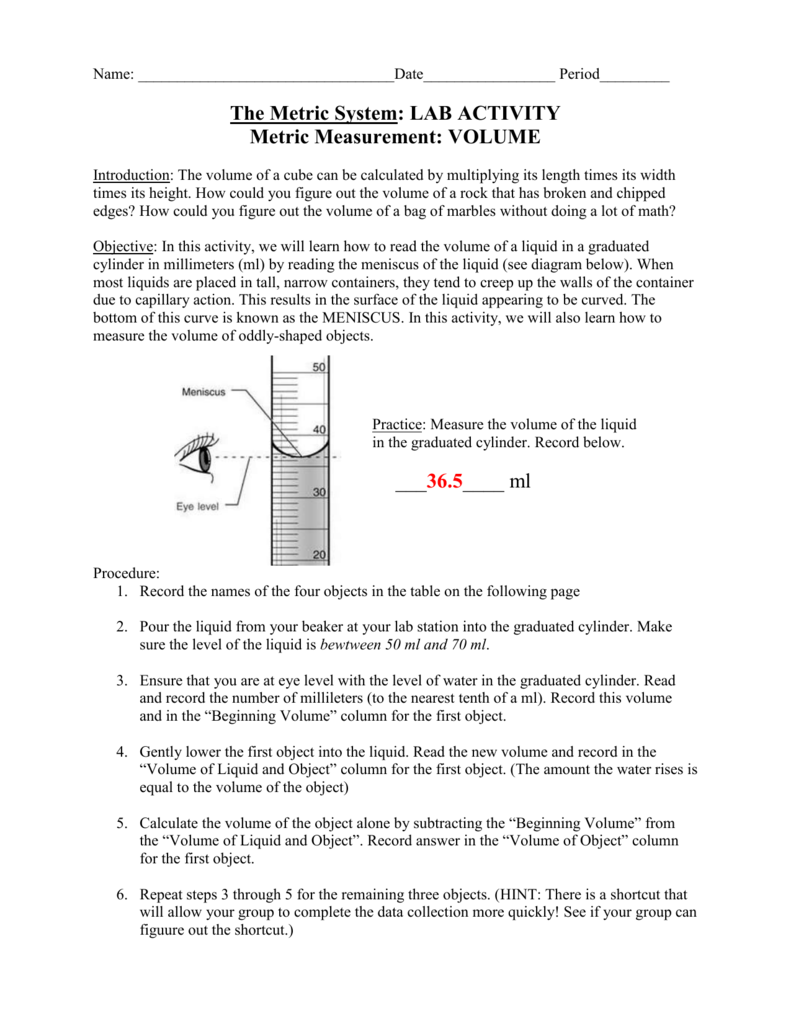
They should fill the cylinder to 10 ml meniscus is on the 10 ml mark and count the number of drops it takes to reach 11 ml.
Marbles in cylinder lab answers. The jar is not filled all the way to the top. You placed extra identical marbles in the cylinder and obtained the data below. Did anything unexpected occur. Continue adding marbles to the cylinder.
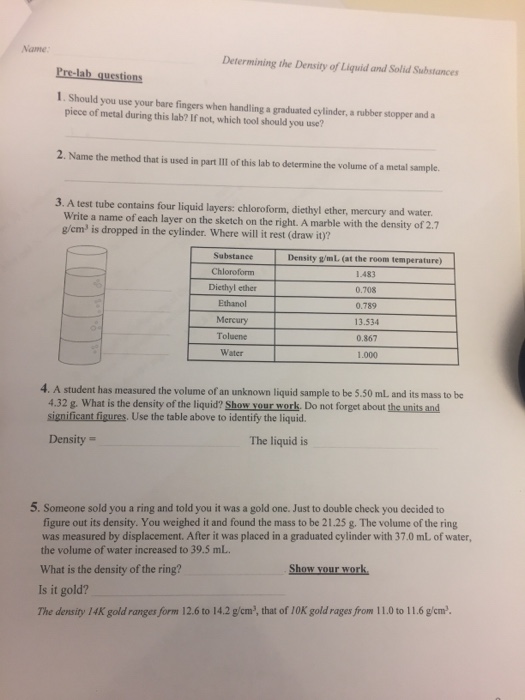
Follow the directions to find the volume of three marbles using water displacement. You placed extra identical marbles in the cylinder and obtained the data below. My students usually end up with a volume of 5 6 ml for three marbles. Volume of water and 12 marbles in cylinder ml volume of 12 marbles ml mass of 12 marbles from part b g density of the marbles mass volume g ml 2010 advanced instructional systems inc.
And north carolina state 2. 1 add 20 ml of water to a 100 ml graduated cylinder. You placed extra identical marbles in the cylinder. Graphing and line of best fit.
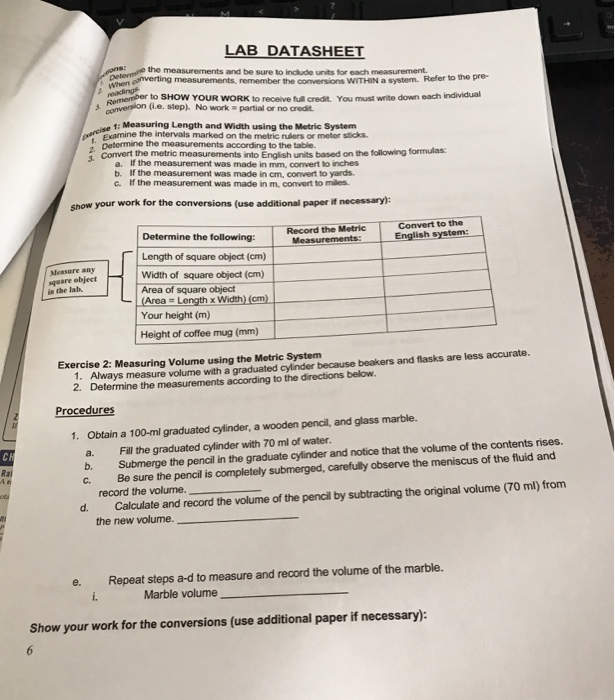
First you need to fill the graduated cylinder with water enough so the marble will be submerged. Use the data to. We cannot remove the marbles from the jar 2. Start at 80 ml and add 2 ml per marble y 2x 80 7.
2 add three marbles to the cylinder and measure the. M arbles in cylinder lab you received a graduated cylinder with three identical marbles and an unknown amount of water already in it. The biggest problem i encounter is that students count the number of drops to 11 ml. Marbles in cylinder lab you received a graduated cylinder with three identical marbles and an unknown amount of water already in it.
Record this amount in the chart. Marbles in cylinder lab you received a graduated cylinder with three identical marbles and an unknown amount of water already in it. 22 cm tall and a diameter of 11 5 cm the marbles take up 16 cm of those 22 cm each marble has a diameter of 1 6 cm. Then get the volume of the water ex.
Use the data to. Explain to students that they will be going through a series of lab stations that will ask them to look at the physical and chemical properties of substances as they go through reactions.